| Some Stuff |
|
| Some MORE Stuff |
|
|
| Blighted ovum |
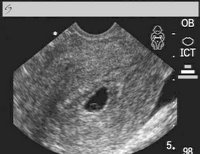
Blighted ovum is also known as anembryonic pregnancy. Nowadays, it is referred to as early pregnancy failure. This condition happens when upon fertilization the egg implants on the uterus but something went wrong in its development. Only the pregnancy sac is present and no embryo can be seen. Because of abnormal development the embryo may have stopped early on in its development or it did not develop at all. This condition is usually seen during the first trimester of pregnancy. It is also a common cause of miscarriage during this stage. Although some women do not even know that that they are pregnant, most are already experiencing the signs of pregnancy like nausea, easy fatigability, sore breasts, etc. Then suddenly there is a mild abdominal cramp or pain like the pain felt during menstruation. This is accompanied by vaginal spotting or bleeding. Upon consultation and ultrasound examination there is only an empty gestational sac. The pregnancy test may still be positive during this time because the hormonal level may still be high. But as the hormonal levels go down the symptoms will start to subside and the pregnancy test will turn negative. Chromosomal problems is the usual cause of this condition. There can either be abnormality in the cell development or there is poor quality of either the egg or the sperm. Oftentimes it is the egg that is of poor quality. If there are no complications or risk of infection the female body is allowed to pass out the tissue on its own with no invasive surgical procedures done. If there is indication, suction curettage or dilation and curettage can be done. The couple is advised to wait for at least 4 to 6 weeks before they try to conceive again. |
|
|
|
| Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia |
This is a molar pregnancy which keeps on coming back. It is usually seen in teenagers and women older than 40. The condition can be benign or malignant (cancerous). There is history of absence of menstruation (amenorrhea) or abnormal duration of menstruation. Sometimes there is passage of the typical hydatid vesicles through the vaginal opening. if the condition has already spread to other organs additional symptoms can be felt depending on the area of metastases. There can be abdominal pain, blood in the urine, or coughing out of blood. The most common areas of spread are the brain, lungs, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and the lower genital tract. After evacuation of the tissue from the uterus it is sent to the laboratory for histopathologic examination. There is no accurate method to predict the behavior of the hydatidiform mole. The only monitoring done is the serum HCG level. In big percentage of cases the condition is benign and the serum HCG level decreases to normal level in 2 to 3 months. A very small percentage of benign cases develop into malignancy. There is no need for therapy in benign cases. The patient is advised to use a reliable method of contraception and the serum HCG level is still monitored weekly to monitor development. In some individuals methotrexate is given as prophylaxis for malignancy. In malignant cases, the serum HCG can go beyond 100,000mlU/ml. This is usually treated with chemotherapy. It is also important to rule out metastasis to other organs hence liver function tests, chest x-ray, and CT scan of head and abdomen are requested. |
|
|
|
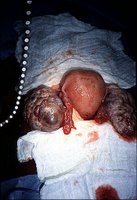
| Molar Pregnancy |

This condition is also known as molar pregnancy. It is an abnormal growth inside the uterus caused by a problem during fertilization. This growth is supposed to develop into a placenta which normally functions to nourish the fetus during pregnancy. That is why the mass is made up usually of placental materials (complete type) or placental tissues and an abnormal fetus (partial type). The patient thinks she is really pregnant because there is also production of the pregnancy hormone called HCG. The precise cause is not yet fully understood. The condition is associated with egg defects and uterine abnormalities. It is common in women more than 40 years old and in those with prior molar pregnancy. The patient manifests vaginal spotting or vaginal bleeding, nausea and vomiting. abnormal size of the uterus with respect to the stage of pregnancy. It can be either too big or too small than what is expected. There can also be heat intolerance, rapid heartbeat, nervousness, tremors in the outstretched fingers, unexplained weight loss which are all signs of hyperthyroidism. Symptoms similar to preeclampsia (presence of protein in the urine, high blood pressure, swelling in legs, ankles, and feet) but occuring in the first trimester of pregnancy almost always indicates presence of H. mole. Ultrasound examination reveals the presence of “cluster of grapes” appearance of placental tissue indicating abnormality of the placenta. Management is done by performing a D&C (dilation and curettage). For older women or those who do not require future pregnancy, hysterectomy or removal of the entire uterus is an option. After any of these procedures, monitoring the HCG level in the serum is done regularly in order that recurrence can be monitored. Follow up visits of the patient to the doctor is a must and the patient is advised to have no pregnancy for at least one year following the procedure. Once recurrence is noted then the patient is advised to have chemotherapy. There is usually a good outcome after treatment. A very low percentage develop into choriocarcinoma. Most cases of H. mole occur after miscarriage, some after an ectopic pregnancy. If a woman wants to know whether she has a molar pregnancy, a visit to a doctor must be done to know her HCG level. |
|
|
|
| Impacted Cerumen |
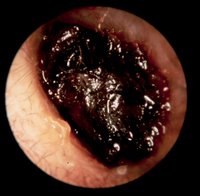
The most common foreign body in our bodies is this condition. Although it is not an emergency, it still warrants immediate removal. Failure to do so leads to its accumulation and hardening which may cause difficulty in hearing. This is very common in school-age children. Busy mothers fail to inspect their children’s ears. Sometimes it’s only an accidental finding during regular physical examinations done in schools. At times, it is the teacher complaining that the child is not listening inside the classroom or is having poor performance in school.
Cerumen is produced by glands located in the external ear canal. It has the advantage of repelling water and trapping dust particles. It becomes impacted due to use of objects put inside the ears which pushes the cerumen towards the inner part of the ear. It then accumulates inside and blocks the eardrum. Another cause may be is overproduction of ear wax.
The removal of the cerumen is done by instilling oil inside the ear canal every night for at least two weeks. This is done to soften the cerumen making removal easier and less painful. After two weeks the child can be brought to a physician who can perform the mechanical removal of the cerumen.
An otoscope with an operating head is usually used. The child must be advised to refrain from moving or must be restrained. Insert slowly a wire loop or wax curette inside the ear canal then slowly scrape the cerumen taking care not to curette the ear canal. This procedure is usually done by an ENT specialist.
Another method is by irrigating the ear canal with water in normal body temperature using a syringe. The jet of water should be aimed along the canal and behind the cerumen in order to push it out. This procedure is usually avoided in children with perforation or with tympanostomy tube.
There are cerumenolytic agents available in the market which can be used to remove cerumen but these sometimes cause severe local reactions especially if not properly used. The best prevention in order not to have impacted cerumen is regular cleaning of the external ear with a washcloth. There is no need to go inside the ear canal using cotton buds, hair pins and the like. The wax that is present inside the ear canal will fall off on its own. |
|
|
|
| Choking in infants |

The Heimlich maneuver I discussed before is not usually done in infants. This is because abdominal thrusts are commonly associated with liver trauma hence are avoided. There are several maneuvers that can be done in infants. These are: Back blows, Chest thrusts, Jaw lift, and Ventilation.
Back blows are done by placing the infant in a head-down face-down position in your left forearm which is angulated to 60 degrees. The head and the neck should be stabilized. The infant’s forearm should be resting on your knee which is in flexed position. While in this position rapidly administer four back blows between the scapulae using the heel of your right hand.
If the back blows fail to remove the obstruction, do the chest thrusts. This is done with the infant in a supine position and lying on a firm surface. Using two fingers of your right hand, place them above the sternum and administer four rapid chest thrusts.
If there is still no breathing lift the jaw of the child in a sniffing position, open the mouth and inspect for presence of foreign body. Do not perform blind finger sweeps inside the child’s mouth as this may aggravate the situation.
Perform mouth-to-mouth resuscitation or bag-mask technique if the above procedures fail. Repeat this procedure several times or you can repeat everything altogether before proceeding to intubation. Intubation or cricothyroidotomy should be done by an expert. |
|
|
|
| Choking |
Choking usually results from foreign body aspiration in the form of small toys, pieces of food like nuts and candies, put inside the nose by little children. These things obstruct the airway when it lodge on the bronchus and the airway obstruction is a medical emergency.
Initially the condition can be asymptomatic or it may cause a mild cough.When severe there can be coughing out of blood with either partial or complete obstruction of the lungs. A chest x-ray can be done but a normal result does not rule out foreign body aspiration nor does it help in improving the condition of the child.
If the child is conscious nothing should be done to dislodge the foreign body. He should be immediately brought to a surgeon who can do laryngoscopy or bronchoscopy.
If the child is unconscious because of airway obstruction, he should be resuscitated immediately by applying up to eight abdominal thrusts (Heimlich maneuver) until the foreign body is dislodged.
This maneuver is done in several ways depending on the age of the child. In a child less than 7 years old, he should placed on his back with you on left his side. Position the heel of your left hand on his abdomen between the umbilicus and the rib cage. Using your hand perform rapid inward and upward thrusts.
In an older child the procedure can be with the child in the same position as above or in sitting or standing position. In the sitting or standing position you should stand behind him, wrap your arms around his waist, and make a fist with your right hand. Your left hand should be grasping the right while making a quick upward thrust in the abdomen. Make sure that the thumb of the right fist is against his midline abdomen slightly below the xiphoid process and above the umbilicus.
This procedure can be done alternately with mouth-to-mouth resuscitation if there is no spontaneous respiration. If the maneuver fails open the mouth and lift the jaw forward.This position improves the respiration in an unconscious child. The head of the child is placed in a “sniffing position” avoiding hyperextension to prevent airway obstruction. A foreign body inside the mouth can be manually extracted using a forcep.
If everything fails then intubation or cricothyroidotomy should be done. This must be done by a surgeon. |
|
|
|
| Anaphylaxis |
Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening allergic reaction to foreign matter. It involves the whole body primarily affecting the circulatory system, respiratory tract, alimentary tract, and the skin. It occurs following exposure to an allergen and the body reacts by releasing substances like histamine.
Histamine is responsible for the vasodilation effect which leads to hypotension or a decreased blood pressure. The movement of fluid into the interstitial space decreases blood volume which may lead to shock. In the lungs fluid may leak into the alveoli producing pulmonary edema hence the difficulty of breathing.
The signs and symptoms seen in this condition are due to histamine and other substances released by the tissues. Airway narrowing produces the dyspnea and wheezing. There are hives and angioedema (swelling underneath the skin) present on the eyelids, lips, or throat which may further narrow down the airway. There may also be vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, abnormal heart rate, palpitation, dizziness,confusion, and cyanosis.
Common allergens include drugs such as penicillin, food such as peanuts, seafoods,or eggs, insect bites, horse serum in the form of vaccines, immunotherapeutic agents, and hormones. They enter the body through inhalation, ingestion, or via injection.
Some drugs cause anaphylactoid reaction. This is an anaphylactic-like reaction resulting from a toxic reaction. It has the same signs and symptoms, complications, and treatment with the trye anaphylaxis.
There is always a previous exposure to the provocative substance. On subsequent exposure an allergic reaction occur followed by onset of symptoms. There is rapid deterioration involving the whole body hence the condition requires immediate medical attention.
Control of airway, breathing, and circulation (ABC) is the first priority. CPR can be done if necessary together with providing an airway by means of endotracheal intubation or tracheostomy. Administer epinephrine as necessary. IV fluids, corticosteroids, and antihistamines are also given. It is very important to identify the allergen in order to prevent future exposure. |
|
|
|
|
|